Preventing the Spread of Hepatitis C
One of the common questions for those with hep C is how do I prevent spreading it? There are many questions during the initial diagnosis of hepatitis C and while your doctor may have explained things to you thoroughly, it is always hard to remember everything that was said.
How is hep C spread to others?
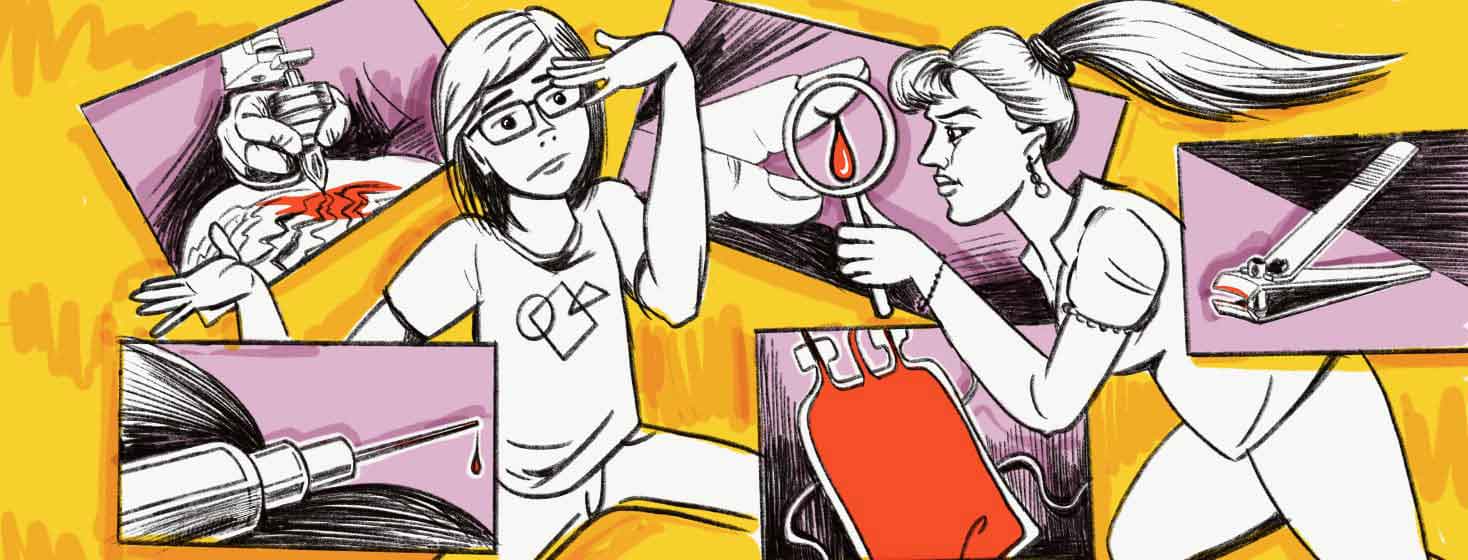
In simple terms, the spread of hep C is by blood. When someone comes in contact with the blood of an infected person, they are then at risk for contracting hep C themselves1.
Each person who contracts hep C has been in contact with someone or an object that was infected by the virus. One of the most common ways hep C is spread is by needle sharing1.
The current opioid addiction rate is so high that more and more hep C is being spread from drug use involving needles, syringes, and other forms of medical equipment1. Hep C can also be spread from a mother to her unborn child1.
What other ways it can be spread?
Contracting hep C can be from razors, sex, tattoos, toothbrushes, nail clippers, and razors. Razors can cut the skin and cause bleeding that a non-infected person could then use and contract1.
Hep C is more passed through male-to-male intimacy, yet still can happen from male/female contact and female/female.
If you choose to get a tattoo and the equipment is not properly sterilized and is used on other clients, you can contract hep C1. Always make sure you are at an approved facility and that you see new equipment being used when getting a tattoo.
Nail clippers are another consideration. They can clip into the skin and if not cleaned and are used by someone with hep C and you then use the clippers, this can cause you to contract the virus1.
Also, a glucose monitor that is used by a person with hep C can carry blood that you may not even see and if you use the monitor you may be infected.
Hairbrushes are also another consideration2. If a person with hep C has scalp lacerations or scabbing from a skin infection or dermatitis, this can cause blood to get on the hairbrush2.
Ways you cannot spread it to others
There are things that you may share with others that will not cause you to get hep C. These things include but are not limited to: sharing water, using the same utensils, hugging each other, kissing, sneezing, coughing, and food sharing1.
What about blood transfers and organ transplantations?
Before 1992, hep C was known to be transferred by blood transfusions, and also organ transplants1. Today, some organ transplants are known as hep C positive donors, and patients are notified that the patient was hep C. Treatment for hep C is offered after the transplant.
Join the conversation