How is Liver Fibrosis Treated?
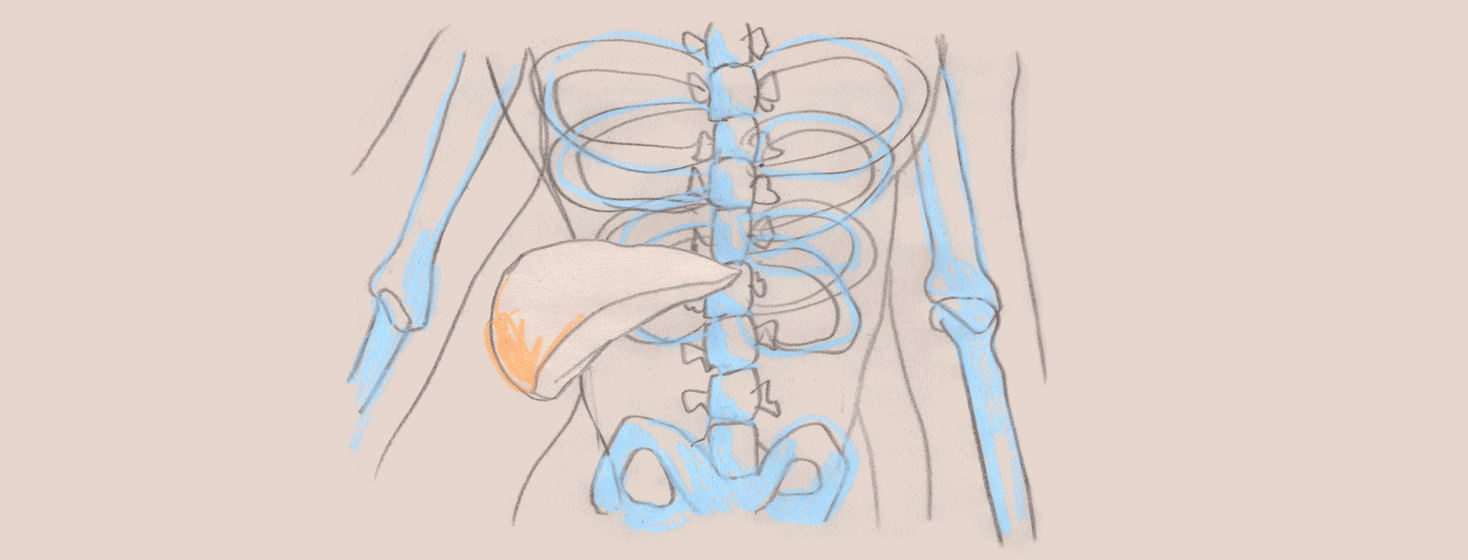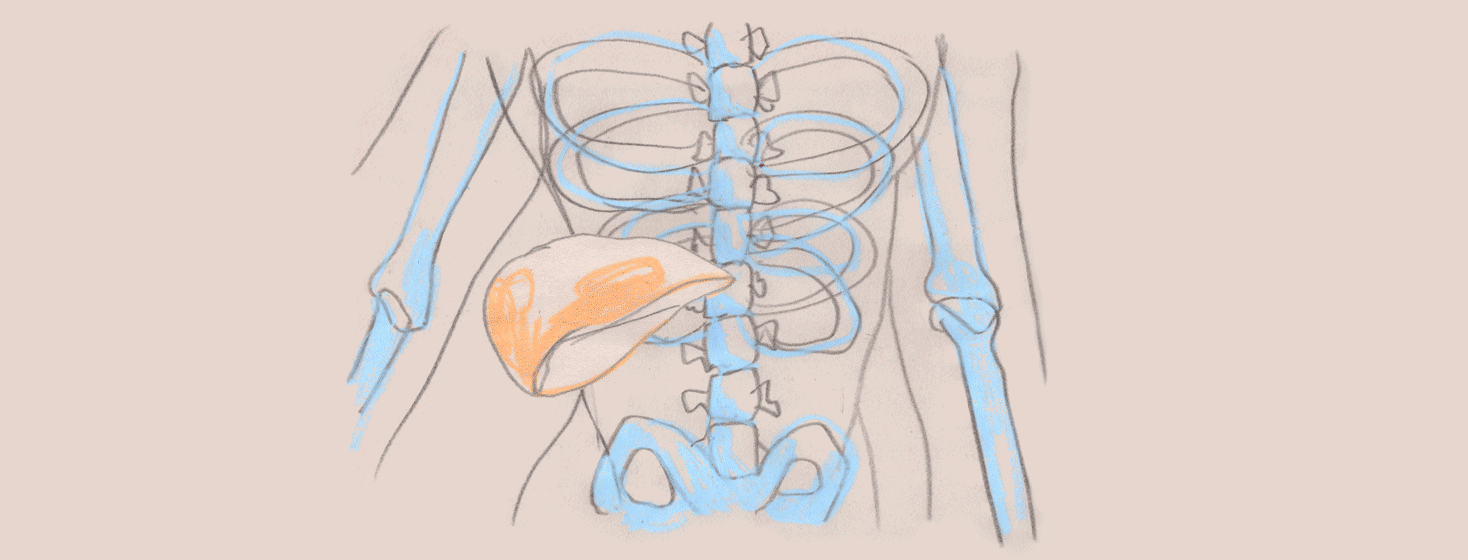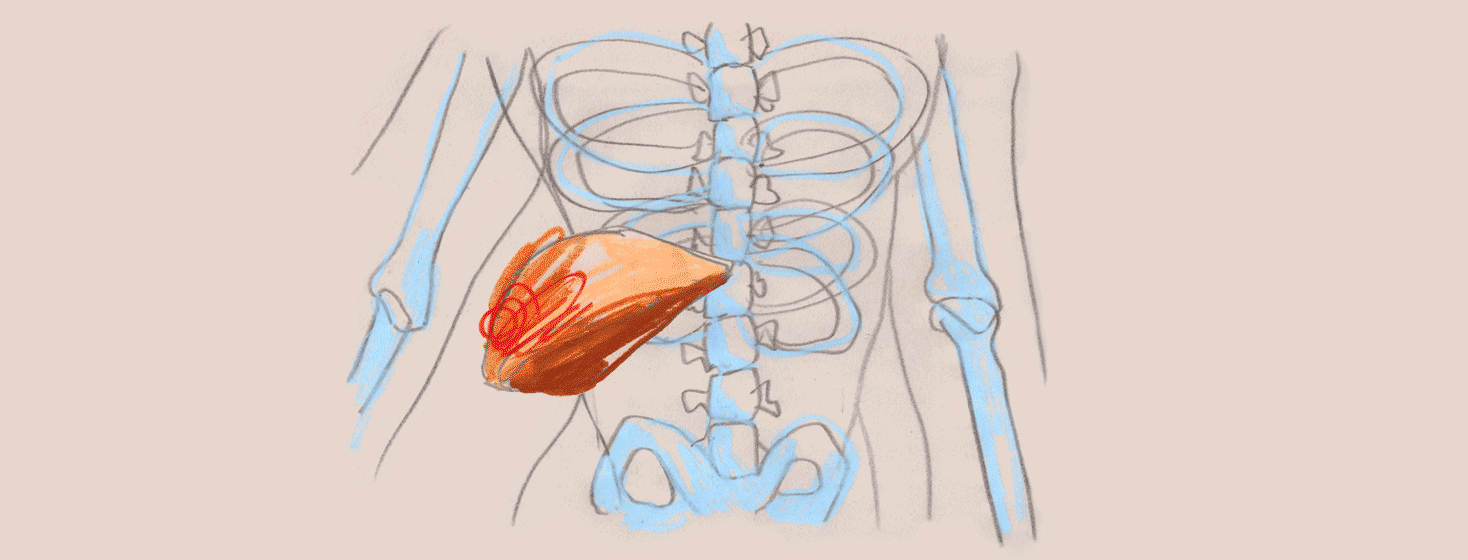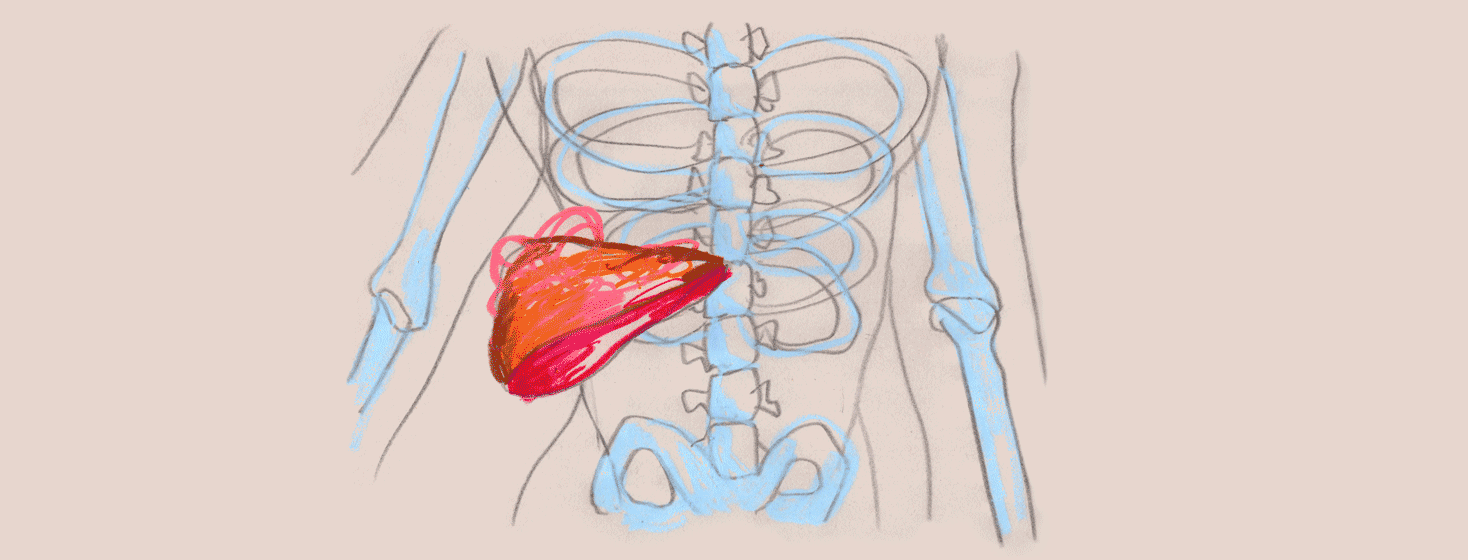
Fibrosis is the scarring that occurs in the liver as a result of repeated injury. When scarring occurs, the liver no longer works the way it should, leading to toxin accumulation in the blood. It was once believed that all stages of liver fibrosis was irreversible, but thankfully, with newer therapies on the market, fibrosis can now be reversed for many people with hep C.
Removing the underlying cause
The most important aspect of treating fibrosis is to remove the underlying cause of liver injury. For people with hep C, the injury is the virus. The virus causes damage to healthy liver cells. By treating the virus, fibrosis can be reversed even after someone has reached the cirrhosis (severe liver scarring) stage.1
To treat the hep C virus, treatment needs to be initiated. Luckily, the treatments for hep C have progressed over the years. They are now safer, have less adverse effects, and often require only 8-12 weeks of treatment. In addition, cure rates tend to be over 90% for these new therapies. For this reason, seeking treatment as soon as possible is one of the best means to treat fibrosis.
It is also generally advised to remove further external factors that may injure the liver, such as high doses of acetaminophen (Tylenol), excessive alcohol intake, and some over-the-counter herbal products.
Reducing inflammation
Because fibrosis is the result of continued inflammation that occurs over a period of several months to years, another key treatment target is to reduce inflammation. There are various drugs that help reduce inflammation. It would be up to the physician to decide if any of these therapies are appropriate for each individual. Interestingly, caffeine found in tea and coffee may be beneficial in treating fibrosis based on its anti-inflammatory properties. All the more reason to continue to drink your cup of jo in the morning!
New therapies
There are multiple new therapies currently in the pipeline for the treatment of fibrosis. These therapies have various targets, such as:2
- Immune modulation - enhancing the immune system to defend against viruses
- Hepatoprotectants - This is a new class of medications that is currently being studied in clinical trials. One of these molecules is hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which has been shown to reduce liver injury.
Liver transplant
Cirrhosis as an end result of the hep C virus is one of the most common reasons for a liver transplant in adults in the United States.3 If the above therapies are unsuccessful in preventing the progression of fibrosis, a liver transplant may be recommended by the doctor. However, being a candidate for a liver transplant does not mean that the individual does not have to undergo further treatments for hep C; Achieving a cure for hep C is required for those who undergo a liver transplant. The treatment can be started either before or after the transplant.
Have you undergone treatment to help reverse fibrosis? Share your experiences below!
Join the conversation